Correlation of left ventricular global longitudinal strain with porcine cell-free DNA in the first & second genetically modified porcine to human xeno heart transplant
Javier Galindo1, Muhammad M Mohiuddin1, Andy A Tully1, Alison Grazioli1, Susie Hong-Zohlman1, Brian Barr1, Timm Dickfeld1, Albert Hicks1, Mohammed Asadi1, Anuj Gupta1, Erika Feller3, Avneesh K Singh1, Dave Ayares2, Bartley Griffith1, Manjula Ananthram1.
1Surgery, University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, United States; 2Revivicor, Blacksburg, VA, United States; 3Cardiology, MedStar, Baltimore, MD, United States
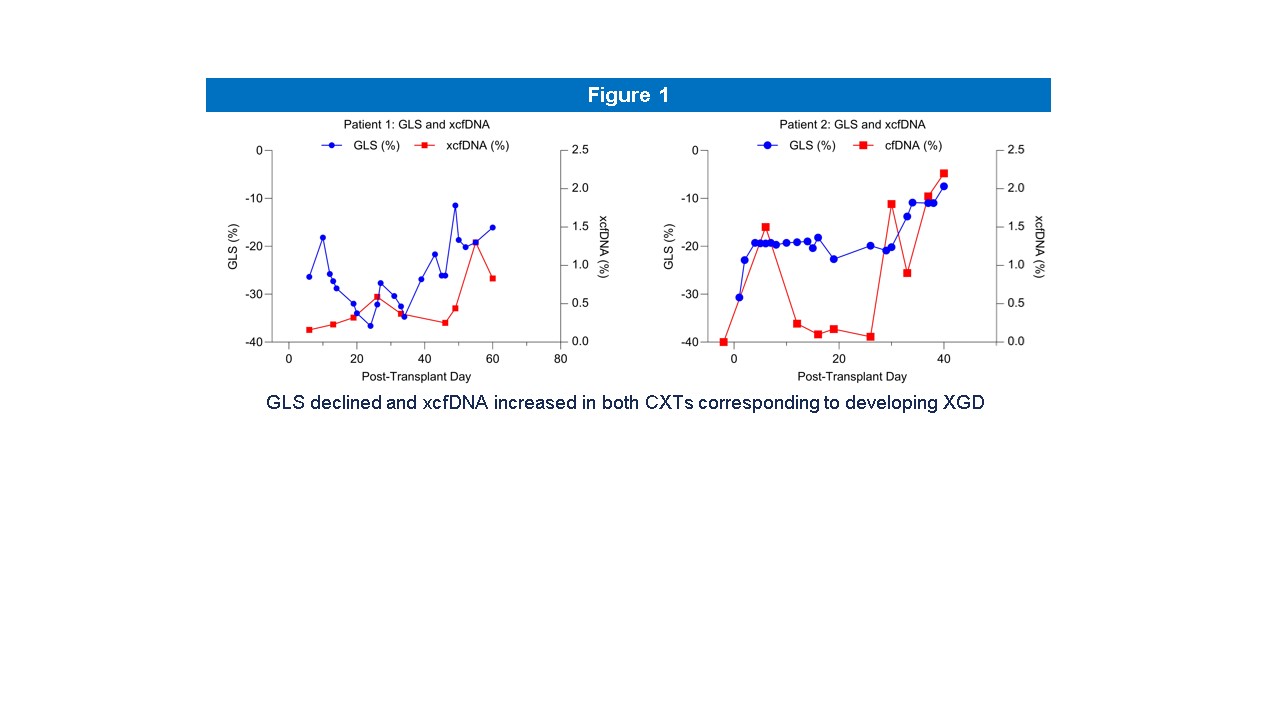
Bacground: Our institution performed two genetically modified porcine to human cardiac xenotransplants (CXT). Patient 1 (P1) & Patient 2 (P2) were declined for allotransplantation & mechanical circulatory support at multiple centers. Left ventricular global longitudinal strain (GLS) is predictive of major adverse cardiac events & all-cause mortality in cardiac allograft recipients. We observed progressive declines in GLS in both CXTs. We hypothesized that GLS would correlate with biochemical markers of xenograft dysfunction (XGD), specifically, xenograft-derived porcine cell free DNA (xcfDNA). We performed a retrospective analysis to address this.
Methods: Serial transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) was performed & cfDNA measurements were obtained (CareDx Inc., Brisbane, CA). TTE was analyzed to calculate GLS. Simple univariate linear regression was performed & Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated using GraphPad Prism 10 (Dotmatics, Boston, MA).
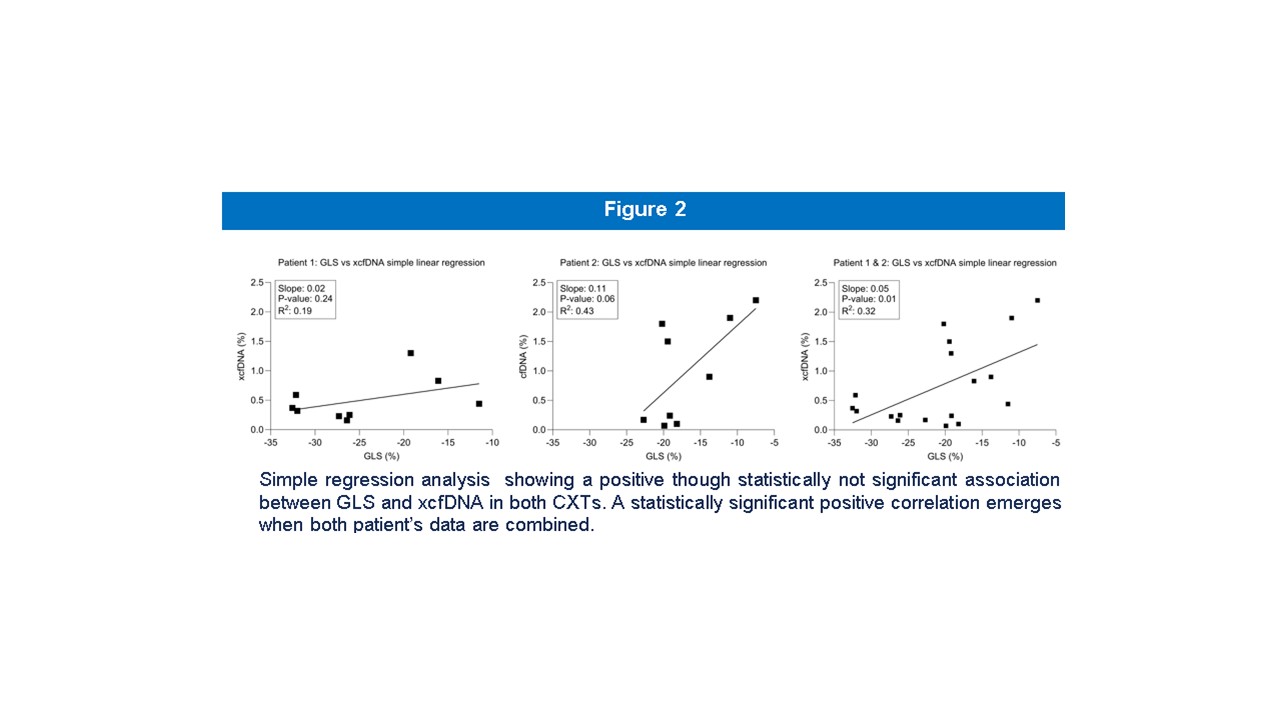
Results: GLS declined to about -10% & xcfDNA rose from negligible to a pre-mortem peak for P1 & P2. Regression analysis showed a modest, non-significant association in P1 &. Pearson correlation coefficient was 0.42 for P1 & 0.66 for P2.
Conclusion: Our results show a modest, non-significant correlation between GLS & xcfDNA in the CXT. A better correlation between GLS & xcfDNA was expected, however the infrequent measurement of xcfDNA is a limiting factor. Both GLS & cfDNA are important in assessing XGD.
[1] Echocardiography
[2] Surveillance
[3] Rejection