Selectin/Integrin blockade and macrophage depletion mitigate injury in pig lung xenoperfusion with human blood
Zahra Habibabady1, Amir Sanatkar1, Megan Dufault1, Sho Takemoto1, Sara De Taeye1, Victoria Diaz1, Jonathan Schulz1, Kristin M Whitworth2, Lars Burdorf3, Will Eyestone3, David L Ayares3, Richard N Pierson III1.
1Center for Transplantation Sciences , Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States; 2National Swine Resource and Research Center, NSRRC, Columbia, MO, United States; 3Revivicor, Inc, Blacksburg, VA, United States
Purpose: This study evaluates whether selectin and integrin blockade, when combined with donor organ gene editing (GE) strategies, can reduce neutrophil and platelet sequestration, RBC damage or inflammatory cytokine elaboration observed during ex-vivo pig lung perfusion with human blood.
Method: GE lungs with 3 carbohydrate antigen knockouts and 6 human transgenes [GalKO.CMAHKO.β4GALKO.hCD46.hCD55.hTBM.hEPCR.hHO1.hCD47] +/- growth hormone receptor (GHR) (10GE, n=16), and GalKO lungs (n=8) were perfused with heparinized fresh human blood. Pigs received DDAVP to deplete vWF. The perfusate was treated with thromboxane synthase inhibitor (1-BIA) and histamine blockers; in some experiments aGPIb Fab was added. Treated lung perfusate received P and E selectin and integrin antagonists (rPSGL1.Fc, GMI1687, IB4), and porcine sialoadhesin blocker (mAb1F1) (10GE, n=8; GalKO, n=4). In seven cases, 10GE left lungs (two with additional HLA-E) were transplanted into baboons, while right lungs were perfused with rPSGL1.Fc, GMI1687, IB4, αGPIb-treated treated human blood; four of these pigs received liposomal clodronate (LC) to deplete resident tissue macrophages. Functional, blood, and tissue analyses were performed at set intervals.
Results: The combined treatment delayed but didn’t prevent neutrophil and platelet sequestration. MCP-1 levels were lower, and RBC fragments and free Hgb were reduced in treated GalKO and 10GE lungs at 4hrs of perfusion compared to controls (Fig 1a-e)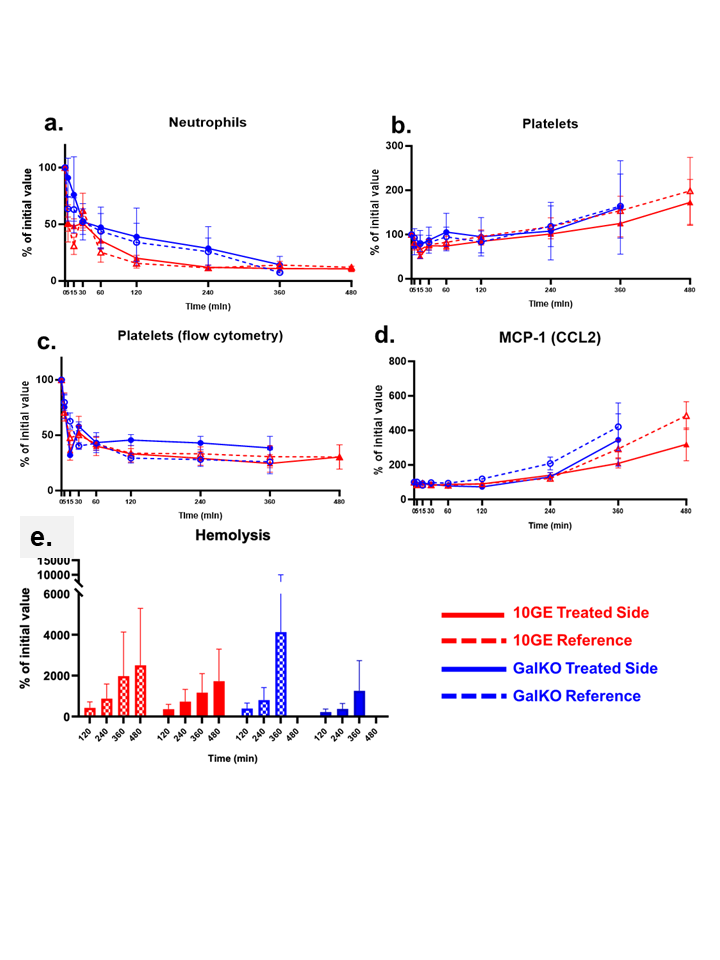 .
.
Lungs from LC-treated pigs showed significantly lower neutrophil sequestration during the first 60 minutes and lower histamine levels throughout the perfusion compared to other 10GE lungs (Fig 2a-b).
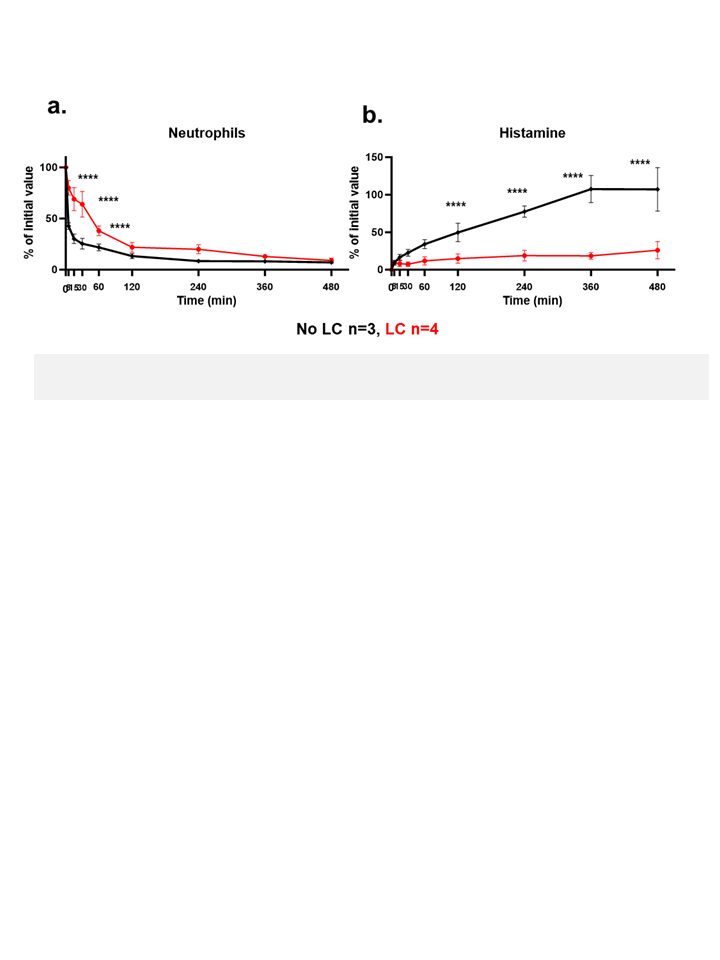
Transplanted 10GE and 11GE lungs showed less parenchymal damage and lower IL-6/IL-8 levels than lungs with fewer genetic modifications, with the longest survival (33 days) observed in a recipient of an 11GE lung from an LC-treated pig.
Conclusion: Selectin and integrin blockade is associated with delayed neutrophil and platelet sequestration and reduced hemolysis and cytokine levels by GE lungs . Pulmonary macrophage depletion with LC may enhance protection and further extend lung xenograft survival.
[1] Perfusion
[2] Inflammation
[3] Macrophage depletion
[4] Neutrophil sequestration
[5] Cytokine reduction
[6] Pig lung perfusion
[7] Selectin blockade
[8] Integrin blockade
[9] Gene editing
[10] Xenotransplantation
[11] Lung injury